Oh how we love character arcs (youtube is full of them). A good protagonist ends up bad, or a bad one turns good. Or, a level-headed character stays that way to meet challenges head-on. News channels love to publish about someone who has ‘fallen from grace’ or done something awful. We all have stories about fallen characters. I am reminded of what the great Apostle Paul said (in Romans 3:23) – “all have sinned, and come short…” In other words, none of us are perfect. We aim to be better (or worse) and our character trends or arcs upwards or downwards, or stays level. An arc is a line that is part of a circle; character arcs are the same and three types are listed below. However, there is another arc you should consider, and it is the arc of electricity makes as it moves from one source to another. A spark arcs as an electrical discharge between two electrodes. We saw that in a spectacular way a few days ago. Our stove caught fire and, when we looked inside, there were sparks arcing at the back of the main oven. In writing, I like to think of this arcing as being between characters. Sparks fly as conflict develops and, as conflict develops, you want to keep reading. Now, back to character arcs:
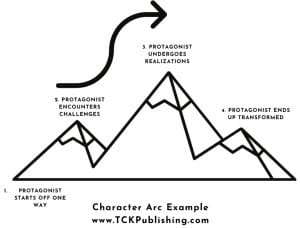
Here are three basic character arcs (source from tkpublishing):
What is a Positive Character Arc?
A positive change arc is one in which the protagonist undergoes a positive transformation. This usually includes a neat resolution at the end, where, because of their internal change, the character finally achieves their goals. An example of a positive character arc in classic literature is that of Marilla, the woman who adopts Anne in Anne of Green Gables. Marilla starts off uninterested in keeping the little girl, but as the story progresses, we see her developing a subtle but strong affection for Anne.
Negative Character Arcs
But not all stories have a happy ending: a negative change arc is one that still shows how your character develops, but not toward a positive transformation. Instead, this arc illustrates a downward spiral. However, the basic “arc” pattern remains the same, as it is still about how your protagonist starts one way and ends up another. Leo Tolstoy’s Anna Karenina is a classic example of a negative character arc. From the beginnings of her adultery, Anna Karenina continues to spiral downward, only to reach a tragic end at the end of the book.
What Is a Flat Character Arc?
Another character arc is the flat arc, wherein the character already has their beliefs in place and uses them to solve problems throughout the story; but even as the story ends, the character remains mostly the same. The development of Miss Maudie, the children’s aunt in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird, is an example of a flat character arc. She remains steadfast in her beliefs from her first scene until the end of the book.
[PS: my main character is an ageing spy who has second-thoughts about the value of his career. I will say no more.]
